Abstract
Introduction
Venetoclax (Ven, a BCL2 inhibitor) combination therapies have been approved for patients with AML. Combinations with hypomethylating agents (HMA) and low dose cytarabine (LDAC) have resulted in durable remissions in certain AML subsets (NPM1/IDH1/IDH2 mutated). While prospective assessment of these combinations is ongoing in MDS and CMML, preclinical and retrospective data in CMML is not encouraging. CMML is highly dependent on MCL1 and frequently possesses features associated with Ven resistance in AML, including disease-defining monocytosis and mutations in the RAS/MAPK pathway. Small retrospective studies of Ven/HMA or Ven/LDAC in patients with CMML have raised similar concern, including our prior study (AJH 2021). Here, we expand upon our prior series with enhanced follow up, as well as the addition of 13 new patients.
Methods
After IRB approval, we retrospectively reviewed our enterprise-wide database for patients with CMML or CMML with blast transformation (CMML-BT, as defined by WHO 2016 criteria) who were treated with at least one cycle of Ven/HMA or Ven/LDAC. Patients who underwent a bone marrow biopsy at the time of diagnosis with available morphology, cytogenetics, and molecular genetics were included. Response criteria for CMML and CMML-BT were defined according to MDS/MPN International Working Group 2015 criteria and European Leukemia Net 2022 criteria, respectively. Categorical variables were compared by Fisher exact test and continuous variables by Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time from initiation of Ven-based therapy to death from any cause and was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Calculations were performed in R (BlueSky Statistics).
Results
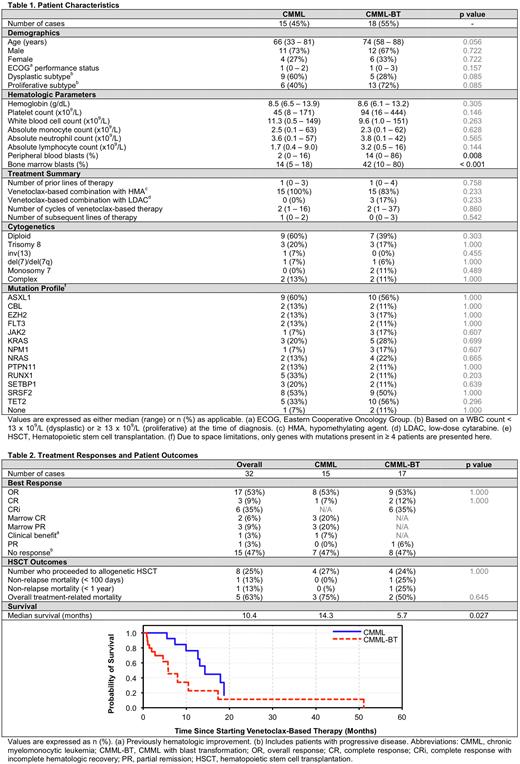
We identified 33 patients with CMML (15) or CMML-BT (18) who met criteria, with baseline characteristics depicted in Table 1. The median age was 73 years (range 33 - 88) with male predominance (70%). The median time from diagnosis to initiation of Ven-based therapy was 13 months (range 0 - 125 months). Common somatic mutations included ASXL1 (59%), SRSF2 (50%), TET2 (47%), KRAS (24%), NRAS (21%), and RUNX1 (21%), with no significant differences in mutational frequency between the two cohorts. Patients received a median of 1 (range: 0 - 4) line of prior therapies, with 12 patients (36%) having received ≥ 2. Seventeen (52%) patients had prior exposure to a HMA - 9 (60%) with CMML and 8 (44%) with CMML-BT.
Combination therapy was administered for a median of 2 cycles (range 1 - 37) and 8 patients (24%) were successfully bridged to allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). The overall response rate (ORR) was 53% (Table 2), not significantly different for CMML (53%) or CMML-BT (53%), with complete response (CR) rates of 7% and 9%, respectively. The median time to best response was 2 months (range 1 - 5) with median duration of response (DOR) estimated at 3 months (range 1 - 35). At last follow up, 2 patients with CMML had ongoing response (one CR and one marrow CR), whereas all evaluable patients with CMML-BT had progressed to other therapies, transitioned to best supportive care, or expired.
After a median follow up of 22 months (range 5 - 126), the median OS for the cohort was 10.4 months. Median OS was significantly longer for patients with CMML as compared to CMML-BT (14.3 vs 5.7 months, p = 0.027). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events included cytopenias (100%), neutropenic fever (12%), tumor lysis syndrome (9%), and spontaneous bleeding (9%) including one fatal spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage. Response prediction was limited by small sample size and, except for a trend towards inferior responses in patients with RUNX1 mutations, there were no clear associations with treatment response/resistance.
Four patients each with CMML and CMML-BT were bridged to allo-HSCT (24% of the cohort). Three CMML patients and two CMML-BT patients died from non-relapse mortality (NRM) within 18 months of HSCT (100-day NRM 25% and 1-year NRM-50%) (Table 2). The remainder are under active surveillance.
Conclusions
Treatment with Ven/HMA or Ven/LDAC combinations resulted in an ORR of 53% in our cohort of 33 patients with CMML (n = 15, ORR 53%) and CMML-BT (n = 18, ORR 53%) with CR rates of < 10%. The median time to best response was 2 months and the median duration of response was 3 months. Eight (24%) patients were successfully bridged to allogenic HCT, although with a high NRM (63%).
Disclosures
Litzow:Abbvie: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Syndax: Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Actinium: Research Funding; Pluristem: Research Funding; Biosight: Other: Data Monitoring Board. Al-Kali:Astex: Other: research support to institution. Foran:AbbVie, Actinium, Aptose, Astex, H3Biosciences, Kura Oncology, Trillium, Xencor: Research Funding; Novartis, Servier, Pfizer, BMS, Taiho: Other: Formal Advisory Activities. Palmer:CTI BioPharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sierra Oncology: Consultancy; Protagonist: Consultancy; PharmaEssentia: Consultancy, Research Funding. Mangaonkar:Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Patnaik:Kura Oncology, Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Venetoclax is a BCL-2 inhibitor that is FDA approved in CLL, SLL, and AML. It is occasionally used off-label in chronic-phase CMML, as described in this work.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal